
Global Handwashing Day is dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of washing hands with soap and water as an effective way to prevent disease. The COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the vital role that hand hygiene plays in preventing the spread of infection and illness.3
Percent reduction in absenteeism due to gastrointestinal illness in schoolchildren6
Percent decrease of diarrheal illness in people with weakened immune systems 4
Percent reduced respiratory illness in the general population 1,5
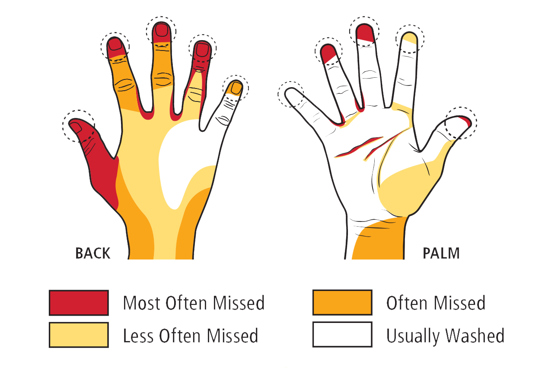
AREAS COMMONLY MISSED DURING HANDWASHING
Fingertips, thumbs and in between the fingers are frequently missed during hand-washing
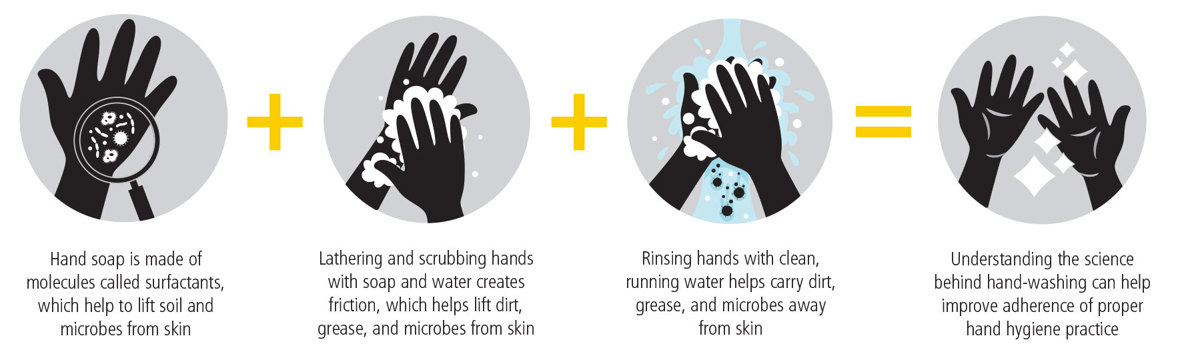
Understanding the science behind handwashing
Although people around the world clean their hands with water, very few use soap to wash their hands.
Washing hands with soap removes germs much more effectively.2

OneShot® Lotion Refill Enriched Lotion Hand Soap with Moisturizers, 1600 mL
Sku: FG4015411
View Details| Item Number | Description |
|---|---|
| FG750196 | OneShot® Lotion Low Profile Dispensers |
| FG402241 | OneShot® Lotion Low Profile Dispensers |
| FG402243 | OneShot® Lotion Low Profile Dispensers |
| Item Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 3486589 | FLex™ Dispenser |
| 3486590 | FLex™ Dispenser |
| 3486591 | FLex™ Dispenser |
| 3486592 | FLex™ Dispenser |
| Item Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 2080802 | AutoFoam Refills |
| FG750112 | AutoFoam Refills |
| 2147031 | AutoFoam Refills |
| 2175515 | AutoFoam Refills |
| 2147027 | AutoFoam Refills |
| 2018595 | AutoFoam Refills |
Rubbermaid Commercial Products offers a complete line of washroom solutions that will ensure that your facility maintains a professional image that leaves every visitor with a positive and lasting impression. Please contact us with product inquiries or questions.
1. Aiello AE, Coulborn RM, Perez V, Larson EL. Effect of hand hygiene on infectious disease risk in the community setting: a meta-analysis.external icon Am J Public Health. 2008;98(8):1372-81.
2. Burton M, Cobb E, Donachie P, Judah G, Curtis V, Schmidt WP. The effect of handwashing with water or soap on bacterial contamination of hands.external icon Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2011 Jan;8(1):97-104.
3. Global Handwashing Day, 2020. Available from globalhandwashing.org/global-handwashing-day/. Accessed 9 October 2020.
4. Huang DB, Zhou J. Effect of intensive handwashing in the prevention of diarrhoeal illness among patients with AIDS: a randomized controlled study.external icon J Med Microbiol. 2007;56(5):659-6
5. Rabie T and Curtis V. Handwashing and risk of respiratory infections: a quantitative systematic review.external icon Trop Med Int Health. 2006 Mar;11(3):258-67.
6. Wang Z, Lapinski M, Quilliam E, Jaykus LA, Fraser A. The effect of hand-hygiene interventions on infectious disease-associated absenteeism in elementary schools: A systematic literature review.external icon Am J Infect Control 2017; 45: 682–689.